If you live in a complex networked environment that usually generates high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and are thinking of protecting yourself but unsure how you have clicked on the right article.
Here you can read everything you need to know regarding a shielded Ethernet cable and how to use this particular type of cable to reduce interference.
So, what is a shielded Ethernet cable? If this is something that you are interested in, ensure to keep reading this article until the end. Let’s begin!

What Is a Shielded Ethernet Cable?
When discussing Ethernet cables, the first thing that comes to people’s minds is the basic unshielded cable.
The reason behind this is that when they hear the term shielded cable, their first thought is what is a shielded Ethernet cable and how it is better than the regular one.
As these questions have become more prominent, especially in the past decade, I wanted to write this article and clarify.
Namely, the most basic definition for the term shielded Ethernet cable is that it is a cable that has an additional outside layer or so-called shield made out of conductive material around the internal conductors.
Knowing that this shield needs to be grounded to cancel the negative effects of EMI (electromagnetic interference) is essential.
Moreover, suppose you are still unsure which cable to choose, the shielded or unshielded, in continuation. In that case, you can read more specifics regarding this cable that will make your decision-making process easier.
What environments require shielded Ethernet cables?
If you have a regular-sized home with an average number of electronic devices, you might not need a shielded Ethernet cable.
The reason behind this is that in smaller businesses or homes, the unshielded Ethernet cables can work just fine without causing any interruptions, as there is usually not enough interference.
On the other hand, if we are talking about large businesses and companies with numerous electronic devices and where there are larger business environments such as elevators, machinery, fluorescent lights, etc., you might need to consider using shielded Ethernet cables.
By utilizing these particular cables, you can reduce the EMI (electromagnetic interference) generated by all the heavy machinery, printers, or air conditioners that can often cause EMI.
So, Ethernet cables are primarily needed in more complex environments with a significant number of electronics and, therefore, significant levels of electromagnetic interference.
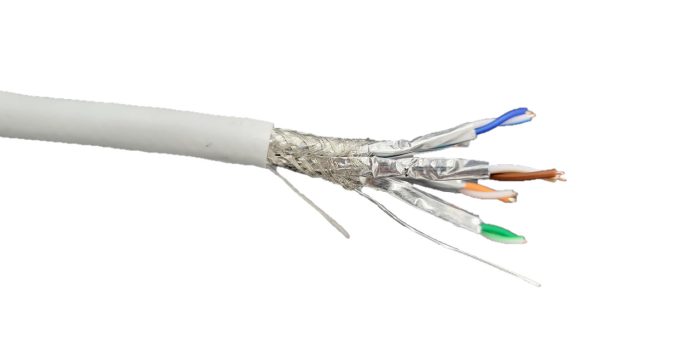
Types of Shielded Ethernet Cables
Now that you know what a shielded Ethernet cable is and the indications for using it, it is time to see the different types of shielded Ethernet cables and their differences.
F/UTP – Foil-shielded cable/Unshielded twisted pair
The first type of a shielded Ethernet cable is the F/UTP which means that the cable is foil shielded, but the twisted pairs in it are unshielded. This cable has an aluminum foil shield beneath the jacket, also known as a screen.
This shield goes through the entire cable and can help dissipate the potential build-up of electrostatic potential. Moreover, the F/UTP Ethernet cable can also help protect the data from nearby sources from the negative impact of electromagnetic interference.
Additionally, one important thing you must know here is that if the drain wire is not grounded correctly, you might encounter opposite effects, meaning the screen might attract unwanted noise, which you want to avoid at any cost. Therefore, it’s imperative that you set up the wire properly and check it for grounding.
S/UTP – Screen shielded cable/Unshielded twisted pair
The second type of shielded Ethernet cable is the S/UTP or the cable with a screen shield, but the twisted pairs in it are unshielded.
The difference between this and the previous type is that instead of foil, this type uses an aluminum braided shield (screen) through the entire cable beneath the jacket.
Thanks to the braided construction of its shield, this Ethernet cable has better protection from RFI (radio frequency interference) and has greater mechanical strength.
F/FTP – Foil shielded cable/Foil shielded twisted pair
When it comes to the F/FTP Ethernet cable, things here are different. Namely, besides this cable having a foil shield under the jacket, the four twisted pairs inside it are also individually wrapped with foil.
SF/UTP – Foil and braid shielded cable/Unshielded twisted pair
Unlike the previous type of Ethernet cable, this one, the SF/UTP Ethernet cable, comes with a double shield under its jacket, meaning it first has a foil wrapping and, on top of it, has a braided shield. At the same time, the four twisted pairs inside the cable are unshielded.
SF/FTP – Foil and braid shielded cable/Foil shielded twisted pair
Finally, the last type of shielded Ethernet cable is the SF/FTP foil and braid shielded cable, meaning this particular type has a double shield under its jacket, a foil, and, on top of it, a braided shield.
The difference between this and the previous type is that the four twisted pairs inside the cable are also individually wrapped with a foil shield.
Advantages of Using Shielded Ethernet Cable
- The shielded Ethernet cables contain much more advanced and beneficial electrical characteristics compared to UTP cables
- The shielded Ethernet cables ensure a complete and uninterrupted data transfer in busier network environments
- The conductive material (the shield) that wraps around the inside of the wire conducts or reflects the external noise away
Do Shielded Ethernet Cables Need to Be Grounded?
I would like to take a brief look at these cables and grounding after seeing: what is a shielded Ethernet cable?
As you have already read, the shielded Ethernet cables work by removing the EMI noise through the grounding process.
This means that setting up these cables must be done by a professional that knows how to properly wire the drain wires because otherwise, you might encounter unwanted consequences and have more EMI noise than before.
